Graph Tutorial
This example shows the ability of graph databases in analyzing and offering recommendations for items that are commonly purchased together. By establishing connections between customer and item vertices using edge collections, the graph is able to accurately deliver tailored recommendations to customers who have bought a particular item.
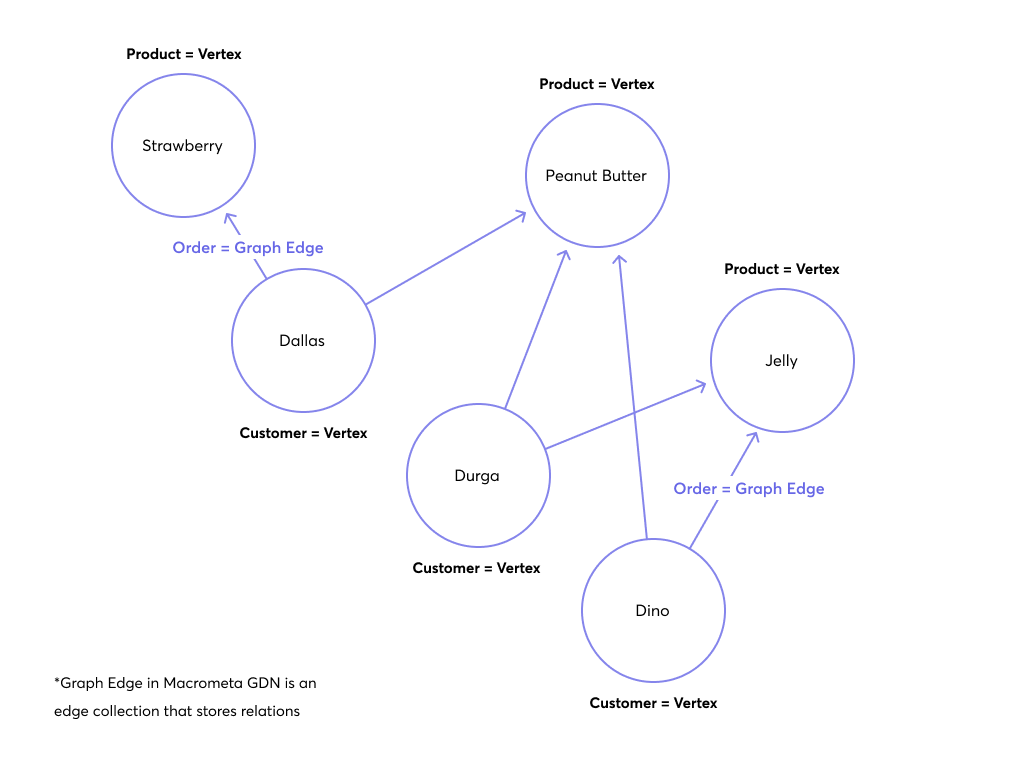
In the graph that we created ,customers Dino and Durga bought the same items. The graph is able to recommend items to Dallas based on the items that Dino and Durga bought. This is a simple example of how graph databases can be used to offer recommendations to customers.
Define Vertices and Edges
For this example we will have two vertex collections - groceryCustomers and groceryItems and one edge collection - groceryOrders. The groceryOrders edge collection will be used to establish a connection between a customer and an item that they bought. Vertex collections are document collections that store the vertices of a graph. Edge collections are graph edge collections that store the edges of a graph, edge collections have the _from and _to attributes that are used to establish a connection between two vertices.
Vertex example in groceryCustomers collection:
{
"_key": "C01",
"name": "John Doe"
},
...
Vertex example in groceryItems collection:
{
"_key": "P03",
"name": "pineapple"
},
...
Graph edge example in groceryOrders collection (Connection between customer C01 and item P03):
{
"_from": "groceryCustomers/C01",
"_key": "4117657795",
"_to": "groceryItems/P03"
},
...
Import the Example Data
If you want to try out the example, you can import the data into your Macrometa GDN account.
Data can be found in the sample-data folder of this repository.
Create two document collections in Macrometa GDN.
groceryItemsgroceryCustomers
Create one edge collection in Macrometa GDN.
groceryOrders
Import test data from sample-data folder to created collections using console. Name of the files are the same as the collection names.
How to Create the Graph on Macrometa GDN
Now that we have the data imported, we can create the graph on Macrometa GDN using javascript SDK.
Prerequisites
- A free trial Macrometa account.
- A Node.js 14+ installation on your local machine. You can download it from here.
- Install the Macrometa javascript SDK.
To check your Node.js version, run the following command in your terminal:
node -v
Create a Graph
- Javascript
const jsc8 = require("jsc8");
client = new jsc8({
url: "https://play.paas.macrometa.io",
apiKey: "xxxxx",
fabricName: "_system",
});
// Edge collections and vertices must be created before running this script.
async function createGraph() {
const response = await client.createGraph("grocery-graph", {
edgeDefinitions: [
{
// Edge collection name --> This collection holds relationships between vertices
collection: "groceryOrders",
// Vertex collection that is used as the start vertex of the edge
from: ["groceryCustomers"],
// Vertex collection that is used as the start vertex of the edge
to: ["groceryItems"],
},
],
});
console.log(response);
}
createGraph();
After we have created the graph, we can start querying it.
How to Query the Graph
Query Explanation
Query for the recommendations for a customer can be done using the following query:
- C8QL
// Query: Recommend the most popular item in the grocery store based on the number of users who purchased it
LET doc = (FOR d in groceryItems FILTER d.name == @name RETURN d)[0]
FOR user IN 1..1 INBOUND doc groceryOrders
FOR item IN 1..1 OUTBOUND user groceryOrders
COLLECT i=item.name WITH COUNT INTO c
FILTER i != @name
SORT c DESC
// LIMIT 2
RETURN {"item": i, "count": c} // item -> number of users who purchased it
// count -> number of times it was purchased
The @name is a bind variable that can be set to any item name. In this example we can set it to peanut butter. First we are filtering by item name and then collecting all the users who purchased that item. Then we are collecting all the items that were purchased by those users. We are filtering out the item that we are looking (peanut butter) for and sorting the result by the number of times it was purchased.
Create Query Worker
It is possible to create a Query Worker on Macrometa GDN using console, javascript SDK, CLI or using the REST API.
You can create Query Worker by yourself or you can use the one that is already created for this example.
Exported Query Worker can be found in the sample-data folder of this repository. It is possible to import the query worker using console. (import-query.json)
After we have created the Query Worker, we can start using it using the following code:
- Javascript
const jsc8 = require("jsc8");
client = new jsc8({
url: "https://play.paas.macrometa.io",
apiKey: "xxxxx",
fabricName: "_system",
});
let itemCustomerSelected = "peanut butter";
async function queryGraph() {
// Query has bind variables that we need to provide as a second argument
response = await client.executeRestql("grocery-recomendations", {
name: itemCustomerSelected,
});
console.log(response.result);
}
queryGraph();
Query Result
When you call Query Worker with peanut butter item as bind variable, the result will be following recommendation:
[
{ item: 'jelly', count: 2 },
{ item: 'napkins', count: 2 },
{ item: 'strawberry', count: 2 },
{ item: 'banana', count: 1 },
{ item: 'milk', count: 1 },
{ item: 'celery', count: 1 },
{ item: 'bread', count: 1 },
{ item: 'white claw', count: 1 },
{ item: 'kiwi', count: 1 },
{ item: 'ketchup', count: 1 },
{ item: 'apple', count: 1 }
]
First recommendation according to this query is jelly which is purchased by two users. Second recommendation is napkins which is purchased by two users. Third recommendation is strawberry which is purchased by two users.
CRUD Operations on Graph
We've demonstrated how to create a graph and perform queries using the Query Worker. With the JavaScript SDK, you can also easily create, read, update, and delete vertices and edges within the graph, allowing for efficient management and interaction with your graph data.
A comprehensive example illustrating CRUD operations on graphs can be found in the repository. Explore the repository to learn more about implementing these operations and harnessing the full power of the Macrometa platform.
Example Data Set
Grocery Customers collection sample. (groceryCustomers)
{
"_key": "C01",
"name": "John Doe"
},
{
"_key": "C02",
"name": "Jane Smith"
},
{
"_key": "C03",
"name": "David Lee"
},
{
"_key": "C04",
"name": "Amanda Chen"
}
...
Grocery Items collection sample. (groceryItems)
{
"_key": "P01",
"name": "orange"
},
{
"_key": "P02",
"name": "strawberry"
},
{
"_key": "P07",
"name": "apple"
},
{
"_key": "P05",
"name": "beer"
}
...
Grocery Orders collection sample. (groceryOrders -> this is an edge collection)
_from and _to are specific fields of edge collection.
{
"_from": "groceryCustomers/C01",
"_key": "4117657795",
"_to": "groceryItems/P03"
},
{
"_from": "groceryCustomers/C02",
"_key": "4117657796",
"_to": "groceryItems/P10"
},
{
"_from": "groceryCustomers/C03",
"_key": "4117657797",
"_to": "groceryItems/P02"
},
{
"_from": "groceryCustomers/C04",
"_key": "4117657798",
"_to": "groceryItems/P09"
}
...