k Shortest Paths Queries
A k shortest path query is a graph traversal algorithm used to find the top k shortest paths between two vertices in a weighted graph. In other words, these queries identify multiple paths between a starting vertex and a destination vertex, ranked by the sum of the weights (such as distances or travel times) of their edges. The paths are sorted in ascending order, with the shortest path first, followed by the next shortest path, and so on, up to the Kth shortest path.
You can use k shortest path queries to find multiple optimal routes between two points based on various criteria such as travel time, distance, or any other custom weight assigned to the edges in a graph. This is particularly useful when you want to provide alternate routes or recommendations for points of interest, taking into account various factors that might affect the path selection.
When executing k shortest path queries in Macrometa GDN, you can use the built-in graph traversal functions provided by the C8QL query language to specify the starting and destination vertices, the weight attribute of the edges, and the maximum number of paths (K) to return. This enables you to efficiently retrieve multiple optimal paths in your application based on the graph data stored in the Macrometa GDN.
For more information about Macrometa queries in general, refer to Queries and Query Workers.
Use Cases
Here are a some use cases for k shortest paths queries.
E-commerce and Retail
- Supply Chain Optimization: k shortest path queries can identify alternative routes for transporting goods from suppliers to distribution centers, considering factors like cost, time, and reliability, ensuring a more efficient and resilient supply chain.
- Personalized Product Recommendations: k shortest path queries can help discover different paths to recommend products based on customer preferences, browsing history, or purchase patterns by analyzing the relationships between products and customers.
Video and Digital Media
- Content Delivery Network (CDN) Optimization: k shortest path queries can find optimal paths for delivering video content to users, considering factors like latency, server load, and network conditions, ensuring a smooth streaming experience.
- Live Event Streaming: When broadcasting live events, k shortest path queries can be used to find reliable transmission paths from the event location to distribution points or viewers. This ensures redundancy and minimizes the risk of service interruption due to network failures or congestion.
Gaming and E-sports
- Matchmaking and Team Balancing: k shortest path queries can find alternative ways to balance teams or match players based on skill level, geographic location, or other factors, creating fair and enjoyable gameplay.
- Dynamic In-Game Navigation: k shortest path queries can be used for pathfinding in video games, offering different routes for characters to navigate through a game world, providing a more engaging gameplay experience.
Financial Services
- Risk Management: k shortest path queries can identify routes of exposure to risk, considering factors like counterparty relationships, credit risk, and market risk, helping financial institutions better understand their risk profile and make more informed decisions.
- Portfolio Diversification: k shortest path queries can analyze relationships between different investment assets to identify alternative paths for diversifying a portfolio, balancing risk and return.
- Fraud Detection: k shortest path queries can help identify unusual patterns in financial transactions, which may indicate potential fraud. By considering different paths between entities, investigators can better understand the relationships between suspicious transactions and trace the flow of funds.
Telecom and IoT
- Network Slicing Optimization: k shortest path queries can identify multiple alternative paths for allocating network resources to different slices, ensuring efficient resource sharing and minimizing the impact of network congestion or failures on various services.
- 5G Traffic Load Balancing: k shortest path queries can discover multiple routing options for network traffic, allowing operators to balance the traffic load across different paths, reducing congestion and optimizing network performance.
- IoT Device-to-Device Communication: k shortest path queries can identify multiple communication paths between IoT devices, enabling redundancy and resiliency in case of device failures or network congestion, and ensuring reliable data exchange.
K Shortest Path Query in Action
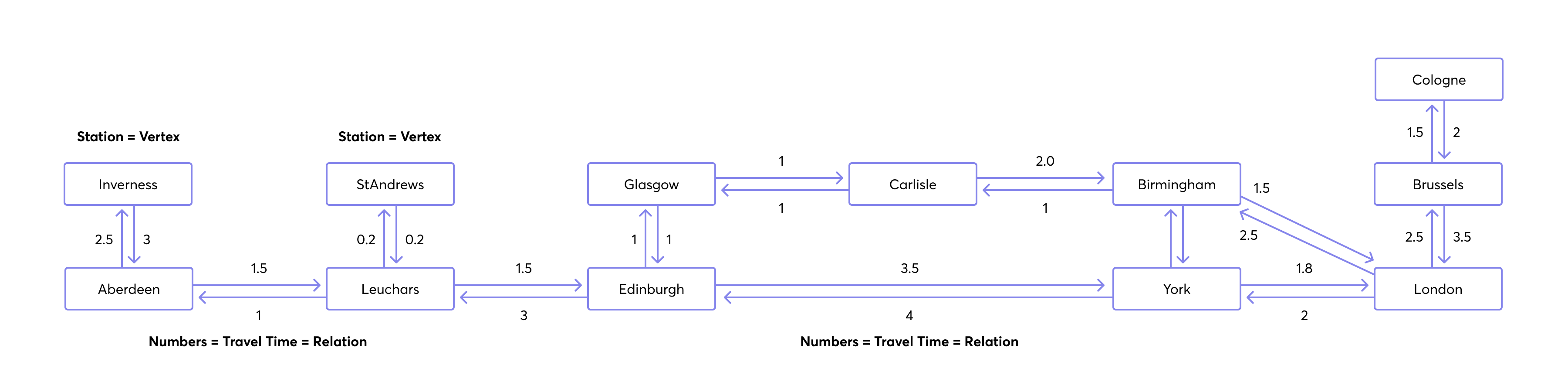
In this high-level example, a graph represents train stations and connections between cities. Each ellipse stands for a train station with the city name included in the station name (the vertices of the graph). Arrows represent train connections between cities (the edges of the graph), and the numbers near the arrows indicate the travel time between stations (used as edge weights).
Shortest Path
Assume a traveler wants to go from Aberdeen to London by train. The shortest path is expected to have the following vertices in this order:
- Aberdeen
- Leuchars
- Edinburgh
- York
- London
The weight of this path is: 1.5 + 1.5 + 3.5 + 1.8 = 8.3.
Alternative Paths
Now, consider alternative paths due to the unavailability of the direct connection between York and London.
Path via Carlisle and Birmingham
An alternative path, which is slightly longer, goes like this:
- Aberdeen
- Leuchars
- Edinburgh
- York
- Carlisle
- Birmingham
- London
The weight of this path is: 1.5 + 1.5 + 3.5 + 2.0 + 1.5 = 10.0.
Path via Glasgow
Another route goes via Glasgow. This path has seven stations, but it's quicker if you compare the edge weights:
- Aberdeen
- Leuchars
- Edinburgh
- Glasgow
- Carlisle
- Birmingham
- London
The weight of this path is: 1.5 + 1.5 + 1.0 + 1.0 + 2.0 + 1.5 = 8.5.