Fulltext Search
Macrometa GDN Search is a full-text search engine that supports key values, documents, and graphs as data models. Compared to a full-text index, Macrometa Search is more configurable and customizable, combining Boolean and generalized ranking retrieval techniques to refine your search results. All Boolean-approved results are ranked by relevance to the respective query using the Vector Space Model in conjunction with BM25 or TF-IDF weighting schemes.
GDN Search is equipped with a state-of-the-art indexing and search facility that enables users to perform sophisticated search operations on multi-model data storage including key-value pairs, documents, and graphs. You do not need to reformat data to make it compatible with GDN search.
Features
GDN Search provides the following capabilities:
- Complex searches with Boolean operators
- Relevance-based matching
- Phrase and prefix matching
- Custom ranking and relevance tuning
- Configurable analyzers and tokenization
- Retrieval of both documents and projections of documents
- Combinable search queries with multiple supported data models & access patterns
- Geo-replicated search indexes for instant results
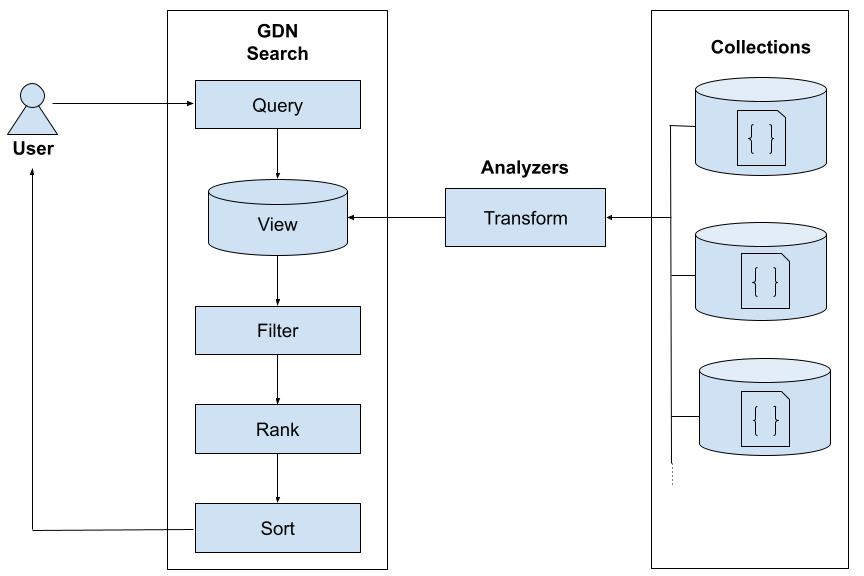
Views and Analyzers
We provide search views and analyzers that boost the efficiency of your search queries:
A search view is a virtual collection that provides fast full-text searching over multiple linked collections.
An analyzer parses input values and transforms them into sets of sub-values for the following use cases:
- Tokenization (splitting text into words and normalizing them).
- Language-specific word stemming.
- Case conversion.
- Removal of diacritical (accent) marks.
Fulltext Search Queries
Fulltext search view features are integrated into C8QL as a SEARCH operation and a set of C8QL functions. Some use cases include:
- Perform federated full-text searches over product descriptions in a web shop with product documents stored in collections.
- Retrieve information in a research database and rank it by relevance based on term frequency (TF-IDF) using case and accent insensitive stemmed phrases with irrelevant terms filtered out.
- Query a data set of movies for titles with words in a particular order and optional wild cards. Sort the results by best matching (BM25) but favor movies with longer duration.
For more information, refer to Fulltext Search Queries.